EDUCATION |
WHAT IS STC? Technically speaking, STC stands for Sound Transmission Class, which is the measurement used to calculate the effectiveness of soundproofing materials in reducing sound transmission between rooms. STC is measured roughly by the decibel reduction in noise a material/partition can provide, abbreviated 'dB'. Simply put, it measures how much sound a wall, for instance, will block from getting through to the other side. STC ratings were introduced in 1961 as a way to compare different types of walls, ceilings, floors, doors, and windows. By taking the transmission loss values and testing them at 18 of the most common frequencies (between 125 Hz-4000Hz), a curve is created, which is then compared to the standard STC curves of reference. Whichever curve of reference your curve most closely matches is the STC rating for your specific fixture. For example, if the curve created by one of your walls most closely matches the standard STC 40 curve, your wall will be said to have an STC of 40. Generally speaking, the higher the STC rating, the more effective a material is at blocking sound at the most common frequencies.
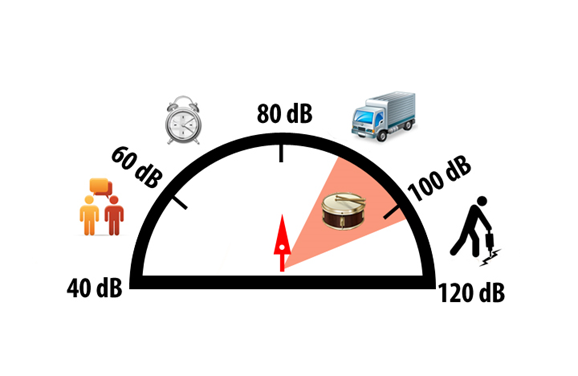
WHAT ARE DECIBELS? Decibels noted as dB, are a simple measurement of how loud something is. On a Sound Pressure Scale, with 0dB being the threshold of audibility and 130dB causing physical pain when listening, most quiet homes register at 40dB.
WHAT IS FREQUENCY? Frequency, by definition, is the measurement of the tone or musical note of the sound. A really high sound, like a flute, registers at 2000Hz whereas a really low sound, like a tuba, registers under 30Hz. It’s important to note that humans can only hear sounds between 20Hz and 20,000Hz- a range that shrinks as people get older.
WHAT IS TRANSMISSION LOSS? Transmission loss is the measurement of the volume (dB) difference on either side of a wall. Let’s say there is a loud sound on one side of your wall (maybe your son playing the drums) that registers at 100dB. We go to the other side of your wall and measure the volume there, and that only registers at 75dB. The difference between the two walls is 25dB, so we could say there is a 25dB transmission loss, meaning 25dB less sound made it to the other side of the wall. The interesting thing about this type of measurement is that the same wall may have a different level of transmission loss if the pitch changes. So even though there might be 25dB less sound when your kid is playing the drums, there may only be 4dB of sound loss when someone is vacuuming in the same room. |